Boron (B) Nutrient Map - Sample
Interpretation
Boron (B) is a vital micronutrient involved in cell wall formation, pollen development, and the movement of sugars and nutrients within the plant. Its role is especially critical during the reproductive stages of crops.
💡 Tip: Boron is highly mobile in soil water and can leach easily, especially in sandy soils or with heavy rainfall. Monitoring is essential during key growth stages.
This map presents the spatial distribution of B levels in crop tissues, helping ensure timely interventions to support flowering and grain set.
📊 Boron Levels & Interpretation
The numbers shown in this table may change depending on the type of crop analyzed and its consequently stage.
| Level | Range (mg/kg in dry matter) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | < 4 mg/kg | Severe deficiency. Can lead to poor flowering, sterility, and malformed tissues. Immediate correction is crucial during early reproductive phases. |
| Low | 4 – 12 mg/kg | Suboptimal levels. May not show symptoms immediately but can reduce yield potential, especially in boron-sensitive crops. |
| Medium | 13 – 19 mg/kg | Adequate for most crops. Supports strong structural development and optimal reproductive growth. |
| High | 20 – 25 mg/kg | Sufficient and balanced. Ensures robust plant structure and efficient sugar transport. |
| Over-sufficiency | > 25 mg/kg | Excess levels. Risk of toxicity, especially in sandy or low-organic-matter soils. Monitor closely. |
| Irregular Material | – | Crops in this area exhibit heterogeneous nutrient profiles and biomass, indicating great variability in field conditions. Further analysis is recommended to better understand these differences. |
🌱 Why Use Boron Crop Maps?
Detect and correct hidden boron deficiencies
Optimize flowering, fruit set, and grain filling
Prevent losses in sensitive crops such as sunflower, canola, corn, and legumes
Align foliar or soil applications with actual field needs
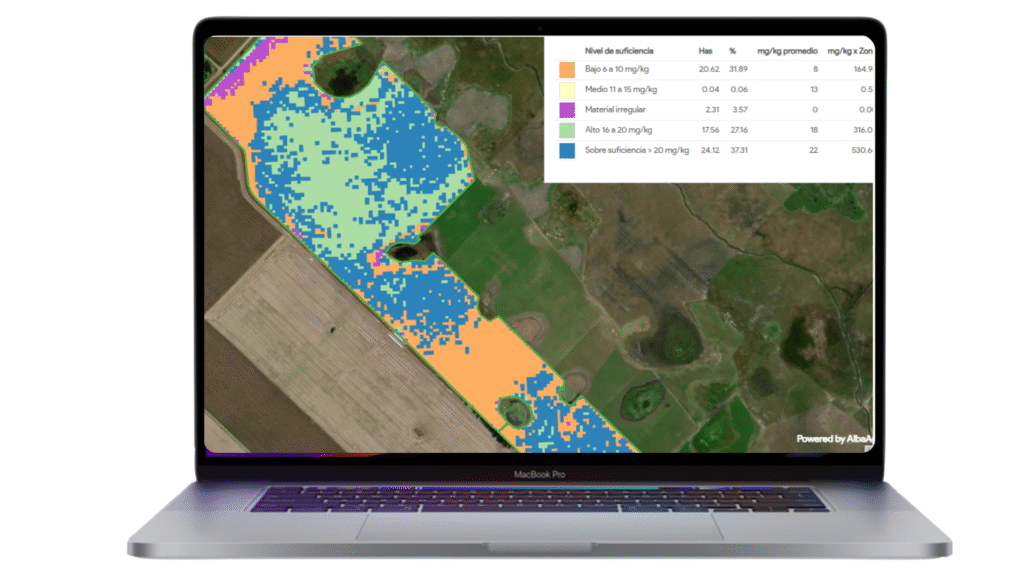
The map in the image shown above corresponds to the wheat crop in its pre-flowering stage.- Maps are available in 10 x 10 m and 3 x3 m pixel resolution.
 Table of contents including detailed parameters.
Table of contents including detailed parameters. Time lapse graphics to evaluate trends and deviations.
Time lapse graphics to evaluate trends and deviations.