🧪 Calcium Content in Soil
Interpretation Guide
We classify calcium (Ca) levels in soil based on their impact on crop performance and nutrient balance:
📊 Calcium Levels
1–4% → Low: Production-limiting
5–8% → Moderate
8–12% → Optimal
12–15% → High: May limit crop performance
>15% → Excessive: Prevents uptake of Mg (Magnesium), K (Potassium), and affects water flow
🔍 What Each Level Means:
🟥 Low (1–4%)
Crops often show visible calcium deficiency (leaf-level symptoms)
Poor infiltration and water retention
Reduced accumulation of usable water in the root zone
🟧 Moderate (5–8%)
May or may not limit crop performance
Deficiencies may appear under low rainfall
Under moderate or high rainfall, crops may perform normally
🟩 Optimal (8–12%)
Supports high crop growth rates
Encourages water retention
Promotes healthy soil structure
🟨 High (12–15%)
Begins to interfere with the uptake of Mg, K, and S
Imbalance may occur, especially in dicot species
🟥 Excessive (>15%)
Strongly restricts the absorption of magnesium, potassium, and sulfur
Affects nutrient balance and water movement
Makes crop management more complex
📌 Note: Calcium plays a crucial role in soil health, but excess can be as limiting as deficiency. At Alba Agro, we help you find the right balance to optimize growth and nutrient uptake.
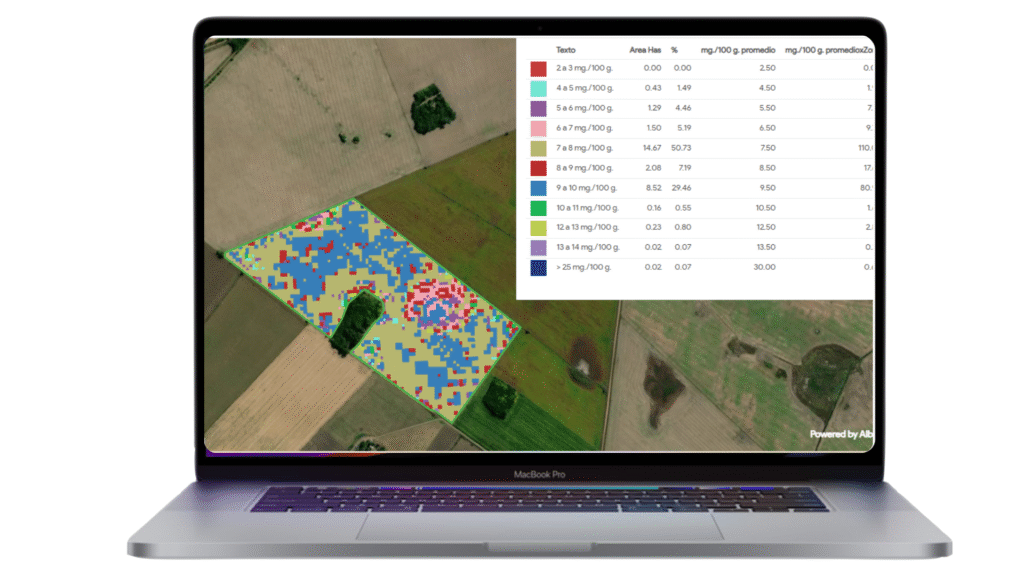
- Maps are available in 10 x 10 m resolution.
 Available images every 5 days.
Available images every 5 days. Table of contents including detailed parameters
Table of contents including detailed parameters Time lapse graphics to evaluate trends and deviations.
Time lapse graphics to evaluate trends and deviations.